What is a Chemical Compatibility Chart?
A chemical compatibility chart is a diagram that guides the safe storage and handling of chemicals. This diagram indicates how different chemicals react when they come into contact with each other. In case of direct contact or through containers.
Purpose:
In industries and chemical storage areas, safe storage and handling of chemicals is essential. For safe storage of chemicals, chemical compatibility charts are designed that help in identifying chemical storage according to their behavior. It identifies which chemicals can be stored together and which must be kept apart. These charts prevent dangerous reactions that can lead to fires, explosions, and toxic releases.
Some important points show the importance of this chart
- Preventing us from the hazards of chemical dangerous reactions effect.
- This ensures safe storage for chemicals that can be stored for a long time.
- Using this chart we follow regulatory compliance. Many regulatory bodies, like OSHA and EPA, require chemical compatibility charts as safety standards.
- We can enhance operational efficiency and inventory management which reduces the need for extensive storage facilities.
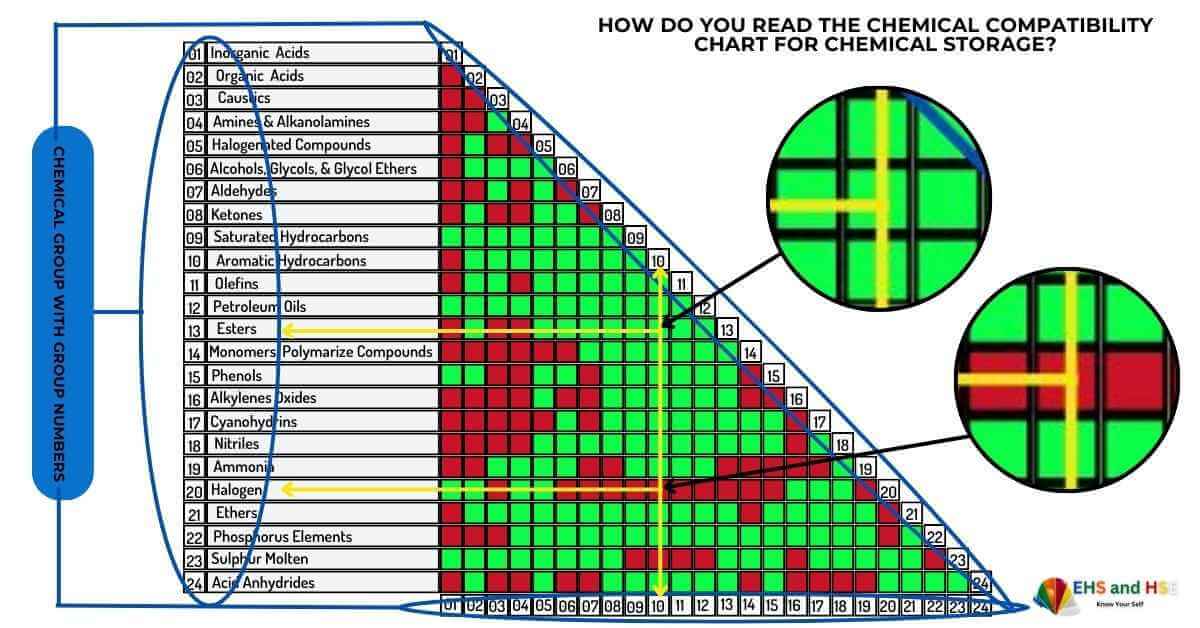
How to read a chemical compatibility chart?
The chemical compatibility chart typically uses a grid format where one axis lists chemicals or chemical groups. The other axis lists the same or other chemicals, providing a cross-reference of compatibility.

As shown in the image, chemical compatibility charts often use symbols and color codes to indicate compatibility or incompatibility.
Green: Chemicals are compatible and can be stored together.
Red: Chemicals are incompatible and must be stored separately.
How to use a chemical compatibility chart?
Here are some steps to use this chart effectively
- Identify Chemicals:
- List all the chemicals you need to store or handle.
- Identify Chemicals Group:
- Identify the groups of all chemicals that you want to store or handle.
- Consult the Chart:
- Locate each chemical on both axes of the chart according to chemical groups.
- Check Compatibility:
- Follow the row and column of each chemical to see if they intersect with a symbol indicating compatibility or incompatibility.
- Take Action:
- Based on the chart, store compatible chemicals together and segregate incompatible ones. Use appropriate storage containers and environmental controls as needed.
List of Chemical groups
- Inorganic Acids
- Organic Acids
- Caustics
- Amines & Alkanolamines
- Halogenated Compounds
- Alcohols, Glycols, & Glycol Ethers
- Aldehydes
- Ketones
- Saturated Hydrocarbons
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Olefins
- Petroleum Oils
- Esters
- Monomers, Polymarize Compounds
- Phenols
- Alkylene Oxides
- Cyanohydrins
- Nitriles
- Ammonia
- Halogen
- Ethers
- Phosphorus Elements
- Sulphur Molten
- Acid Anhydrides
Example Scenario
For example, we need to store hydrochloric acid (HCL) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). By consulting a chemical compatibility chart, we can find that these substances are highly incompatible. Due mixing of HCl and NaOH can produce a violent exothermic reaction. Releasing heat and potentially causing splashes of corrosive liquids. The chart would indicate that these chemicals must be stored separately. And in the well-ventilated areas, and containers resistant to their corrosive nature.
Chemical Compatibility Chart: According to GHS hazards.
Purpose:
The chemical compatibility chart gives guidelines for the safe storage of the chemicals. In this compatibility chart, this GHS hazard pictogram is the base of the storage with associated risks.

How do you read this chart?
This image shows the same behavioral chemicals we can store in the same place. Opposite behavioral chemicals, we can’t store them in the same place.
This chemical compatibility chart also uses a grid format where one axis shows the chemical’s behavior GHS sign. The other axis also shows the same or other chemicals GHS hazards signs, providing a cross-reference of compatibility.

Key Elements of Storage and Handling of Chemicals
| Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Proper Ventilation | Ensure proper ventilation in the chemical storage area to avoid the accumulation of toxic or flammable vapors. Ventilation is very essential. |
| Control Temperature | Some chemicals may become more reactive at higher or lower temperatures. Ensure the storage area temperature according to the safe temperature of chemicals. |
| Container material | Container materials should be safe appropriate stored chemical. Use containers made of materials that do not react with the stored chemicals. |
| Secondary Containment | Have spill containment measures in place to manage accidental releases. It is also called secondary containment and it is made around the storage tanks to control spells. |
| Staff Training | Train your staff on the use of chemical compatibility charts and safe handling practices with appropriate PPEs. |
| Labeling | Clearly label all containers with the chemical name and hazard information. |
| Documentation | GHS hazard pictograms, safety data sheets, and emergency contact numbers should be available in the chemical storage area. |
| Availability of PPEs | Ensure appropriate personal protective equipment is available in the storage area |
| Spell Control Box | A box with all spell control elements should be mounted on the wall at a suitable place in the storage area. |
| Eyewash and Shower | Water shower and eyewash should be available in the chemical storage area |