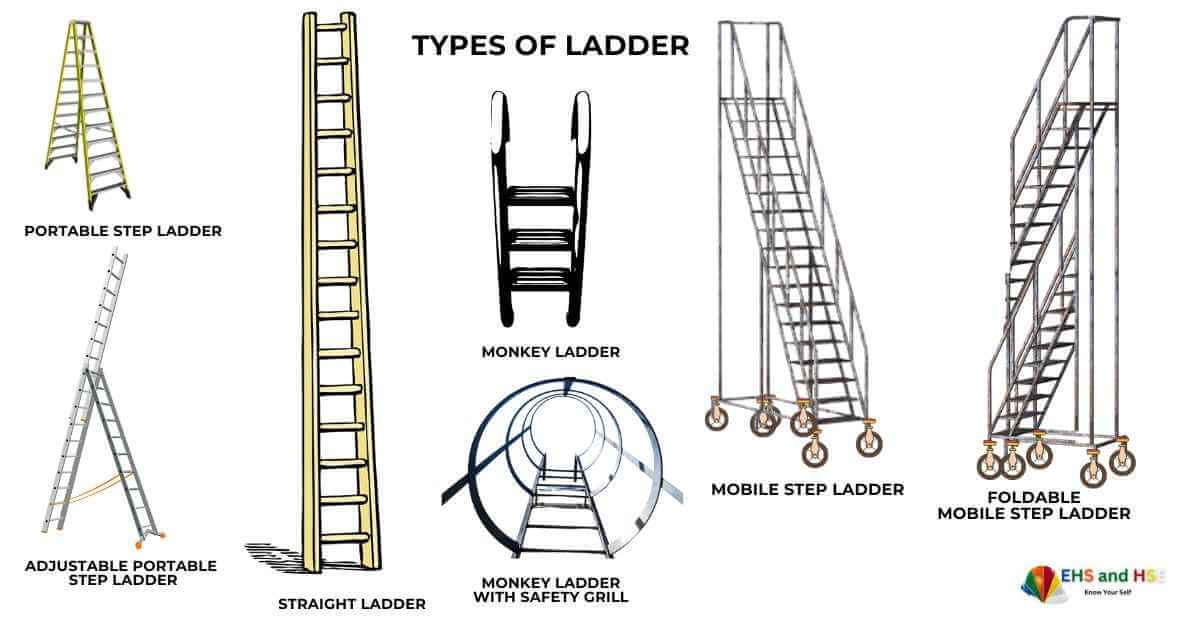
A Personal Evacuation Plan (PEP) is a customized strategy designed to help individuals evacuate safely from a building or area during an emergency, such as a fire, natural disaster, or other emergency situations. This plan takes into account individual needs, abilities, and scenarios to ensure that everyone can respond effectively in the event of an emergency.
Emergency Evacuation Map
The Emergency Evacuation Map guides the workers, visitors, and contractors on the way into the building and coming in going out of the building.
An Emergency Evacuation Map is a map that shows aisle marking on the floor and everything which has volume on the floor. Location of everything on the floor. Emergency Evacuation Map gives importance to exit ways like lifts and stairs in the building.
How to make an Emergency Evacuation Map?
The emergency evacuation map guides the workers and visitors to go out of the building in case of an emergency with safety. The emergency evacuation map highlights the aisle marking, Emergency exit door, normal exit doors, and all equipment related to emergencies.
Creating an effective Emergency Evacuation Map involves several key steps. Here’s a guide to help you design one:
Step-by-Step Guide to Create an Emergency Evacuation Map
- Gather Information:
- Obtain a current floor plan of the building or area.
- Identify all exits, stairwells, and emergency assembly points outside the building.
- Identify Key Locations:
- Mark important areas such as restrooms, elevators (not to be used in emergencies), and disabled access routes.
- Highlight potential hazards (e.g., flammable materials, electrical rooms).
- Designate Evacuation Routes:
- Determine the safest and quickest routes to exits from various locations in the building.
- Ensure these routes are clear of obstacles and accessible for everyone, including people with disabilities.
- Use Symbols and Colors:
- Utilize easily recognizable symbols (e.g., arrows for routes, green for exits, red for hazards) to enhance clarity.
- Consider color-coding different elements for easy identification.
- Add a Legend/Key:
- Create a legend that explains the symbols and colors used in the map for clarity.
- Include Important Information:
- Provide details such as emergency contact numbers, protocols (e.g., “Do not use elevators”), and the location of emergency equipment (fire extinguishers, first aid kits).
- Create Multiple Versions:
- Design maps for different floors or areas of the building to ensure everyone has access to relevant information.
- Test the Map:
- Conduct a drill to see how well the map works in practice and make any necessary adjustments based on feedback.
- Make the Map Visible:
- Place printed copies of the map in visible locations throughout the building (near entrances, hallways, break rooms).
- Consider adding digital versions accessible via building management systems or emergency apps.
- Regularly Update:
- Review and update the map regularly, especially after renovations, changes in layout, or after conducting drills.
Tips for Effectiveness:
- Keep it simple and easy to understand.
- Use a large enough font and clear graphics.
- Make sure everyone in the building is aware of the map and understands how to use it.
- Conduct regular training and drills to create awareness in workers for safe evacuation procedures.
Creating an effective Emergency Evacuation Map can greatly enhance safety during an emergency by helping people navigate quickly.
Types of this map
- Building an Emergency Evacuation Map
- Office blocks
- Production departments
- Workshops
- Power / Boiler houses
- Laboratories / canteen / cafeterias
- Plant / Unit Emergency Evacuation Map

This type of map is designed by EHS or the safety department which mentions everything about safety.
Elements of This Map
This Map highlights the aisle marking and the following things:
Points
- You are Here
- Emergency Exit Door
- Normal Exit Door
- Location of fire extinguishers
- Location of electric panels and board
- Available fire hose cabinet
- Available First aid box
- Smoke detector
- MCP (Manual Call Point)
- Fire and water bucket
Evacuation Policy
The Evacuation Policy of the company is written on the emergency exit map. Any worker, visitor, and contractor read this policy and follow it. This policy is very important and shows the rules of the company. Detailed Evacuation Policy
Evidence

Importance
Emergency Evacuation Map supports the workers and visitors to quickly understand the safe exit ways in case of emergency. The emergency exit plan or evacuation policy can save many workers’ and visitor’s lives.
Location of this map
This map should be located near the main entrance door or the gathering area. Because anyone can find and read this map easily in normal or emergencies.